치춘짱베리굿나이스
[백준] 4992 본문
Hanafuda Shuffle
문제
There are a number of ways to shuffle a deck of cards. Hanafuda shuffling for Japanese card game 'Hanafuda' is one such example. The following is how to perform Hanafuda shuffling.
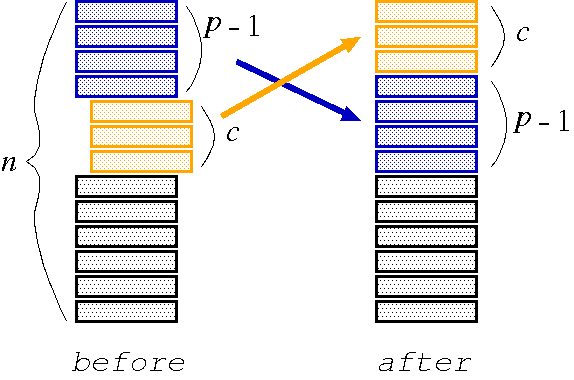
There is a deck of n cards. Starting from the p-th card from the top of the deck, c cards are pulled out and put on the top of the deck, as shown in Figure 1. This operation, called a cutting operation, is repeated.
Write a program that simulates Hanafuda shuffling and answers which card will be finally placed on the top of the deck.
입력
The input consists of multiple data sets. Each data set starts with a line containing two positive integers n (1 <= n <= 50) and r (1 <= r <= 50); n and r are the number of cards in the deck and the number of cutting operations, respectively.
There are r more lines in the data set, each of which represents a cutting operation. These cutting operations are performed in the listed order. Each line contains two positive integers p and c (p + c <= n + 1). Starting from the p-th card from the top of the deck, c cards should be pulled out and put on the top.
The end of the input is indicated by a line which contains two zeros.
Each input line contains exactly two integers separated by a space character. There are no other characters in the line.
출력
For each data set in the input, your program should write the number of the top card after the shuffle. Assume that at the beginning the cards are numbered from 1 to n, from the bottom to the top. Each number should be written in a separate line without any superfluous characters such as leading or following spaces.
풀이
const hanafuda = () => {
let input = require("fs")
.readFileSync("/dev/stdin")
.toString()
.trim()
.split("\n")
.map((n) => {
return n.split(" ").map((m) => {
return parseInt(m);
});
});
let ans = [];
let i = 0;
while (true) {
if (input[i][0] === 0) break;
let arr = Array.from({ length: input[i][0] }, (val, idx) => idx + 1);
let c = input[i++][1];
for (let j = 0; j < c; j++) {
let stackA = [];
let stackB = [];
while (input[i + j][0]-- > 1) stackA.push(arr.pop());
while (input[i + j][1]-- > 0) stackB.push(arr.pop());
while (stackA.length > 0) arr.push(stackA.pop());
while (stackB.length > 0) arr.push(stackB.pop());
}
ans.push(arr.pop());
i += c;
}
console.log(ans.join("\n"));
};
hanafuda();반성회
- 몇번째 카드인지는 스택의 Top부터 센다
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <- 스택의 top
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 <- 번째수- 따라서 3번째 카드부터 5장을 끄집어내고 싶으면
1 2 3 {4 5 6 7 8} 9 10 <- 스택의 top
10 9 8 {7 6 5 4 3} 2 1 <- 번째수- 위 예시에서는 3번째 카드가 8이므로, 8부터 왼쪽으로 5장을 꺼내야 한다
- 먼저 n번째 카드부터 끄집어내기 위해서 n - 1번째 카드까지 스택 A에 push한다
원본배열: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
스택A: 10 9 (1~2번째 카드)- m장의 카드를 스택 B로 끄집어낸다
원본배열: 1 2
스택A: 10 9 (1~2번째 카드)
스택B: 8 7 6 5 4 (3번째 카드부터 5장)- 스택 A의 모든 원소를 원본 배열에 Push한다
원본배열: 1 2 9 10
스택A:
스택B: 8 7 6 5 4- 스택B의 모든 원소를 원본 배열에 Push한다
원본배열: 1 2 9 10 4 5 6 7 8
스택A:
스택B:'Javascript + Typescript > 자바스크립트로 알고리즘풀기' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 10866 (0) | 2022.02.09 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 10845 (0) | 2022.02.09 |
| [백준] 7585 (0) | 2022.02.09 |
| [백준] 7568 (0) | 2022.02.09 |
| [백준] 10814 (0) | 2022.02.09 |

